E D U C A T I O N
PREDIABETES
P R E D I A B E T E S
Learning About Metabolic Syndrome
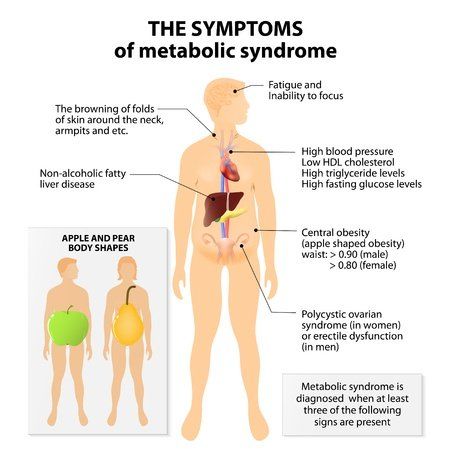
Metabolic syndrome is the name for a group of health problems. It includes having too much fat around your waist and high blood pressure. It also includes high triglycerides, high blood sugar, and low levels of healthy (HDL) cholesterol. These problems make it more likely you will have a heart attack or stroke or get diabetes.
Your family history (your genes) can cause metabolic syndrome. So can unhealthy eating habits and not getting enough exercise.
You can help lower your risk of heart attack, stroke, and diabetes if you eat healthy foods and get more exercise. It may be hard to make these lifestyle changes. But even small changes can help.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
Prediabetes: Care Instructions
Your Care Instructions
Prediabetes is a warning sign that you are at risk for getting type 2 diabetes. It means that your blood sugar is higher than it should be. Most people who get type 2 diabetes have prediabetes first. The good news is that lifestyle changes may help you get your blood sugar back to normal and avoid or delay diabetes. Also, pregnant women who get gestational diabetes may have prediabetes first.
Type 2 diabetes is a disease in which the body does not respond properly to a hormone called insulin. Over time, the body does not make enough of the hormone. Insulin helps sugar from your food enter your body cells to be used as energy.
Without insulin, the sugar cannot get into the cells to do its work. It stays in the blood instead. This can cause high blood sugar levels. A person has diabetes when the blood sugar stays too high too much of the time.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
Insulin Resistance: Care Instructions
Your Care Instructions
Insulin resistance means that the body cannot use insulin properly. Insulin lets sugar (glucose) enter the body's cells, where it is used for energy. It also helps muscles, fat, and liver cells store sugar to be released when needed. If the body tissues do not respond properly to insulin, the blood sugar level rises.
Insulin resistance mainly is caused by obesity, although other medical conditions, such as acromegaly and Cushing's syndrome, also can cause it. It can run in families too.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
Diabetes Warning Signs
Call your doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
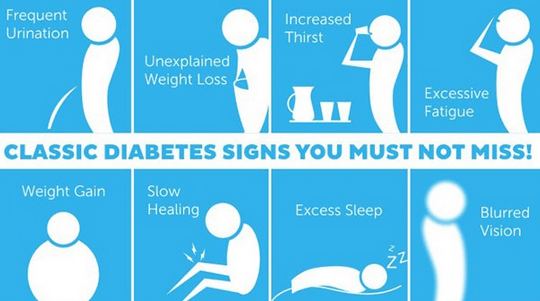
You have any symptoms of diabetes. These may include:
- Being thirsty more often.
- Urinating more.
- Being hungrier.
- Losing weight.
- Being very tired.
- Having blurry vision.
- You have a wound that will not heal.
- You have an infection that will not go away.
- You have problems with your blood pressure.
- Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if you have any problems.
Care instructions adapted under license by Alliance In Health Diabetes Control Center. This care instruction is for use with your licensed healthcare professional. If you have questions about a medical condition or this instruction, always ask your healthcare professional. Healthwise, Incorporated disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information.
LEARN MORE